认识
一、认识
二、mount 初始化阶段
在一次调和的过程中,发现了一个 fiber tag = 1 类组件的情况,就会按照类组件的逻辑来处理。对于类组件的处理逻辑,首先判断类组件是否已经被创建过,
如果未创建,那么这个过程就是初始化阶段,代码如下:
/* workloop React 处理类组件的主要功能方法 */
function updateClassComponent(){
let shouldUpdate
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode // stateNode 是 fiber 指向 类组件实例的指针。
if (instance === null) { // instance 为组件实例,如果组件实例不存在,证明该类组件没有被挂载过,那么会走初始化流程
constructClassInstance(workInProgress, Component, nextProps); // 组件实例将在这个方法中被new。
mountClassInstance( workInProgress,Component, nextProps,renderExpirationTime ); //初始化挂载组件流程
shouldUpdate = true; // shouldUpdate 标识用来证明 组件是否需要更新。
}else{
shouldUpdate = updateClassInstance(current, workInProgress, Component, nextProps, renderExpirationTime) // 更新组件流程
}
if(shouldUpdate){
nextChildren = instance.render(); /* 执行render函数 ,得到子节点 */
reconcileChildren(current,workInProgress,nextChildren,renderExpirationTime) /* 继续调和子节点 */
}
}
2.1 constructor
在mount阶段,首先执行的constructClassInstance函数,用来实例化 React 组件。组件中 constructor 就是在这里执行的
function updateClassComponent(){
let shouldUpdate
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode // stateNode 是 fiber 指向 类组件实例的指针。
if (instance === null) { // instance 为组件实例,如果组件实例不存在,证明该类组件没有被挂载过,那么会走初始化流程
constructClassInstance(workInProgress, Component, nextProps); // 组件实例将在这个方法中被new。
mountClassInstance( workInProgress,Component, nextProps,renderExpirationTime ); //初始化挂载组件流程
shouldUpdate = true; // shouldUpdate 标识用来证明 组件是否需要更新。
}else{
shouldUpdate = updateClassInstance(current, workInProgress, Component, nextProps, renderExpirationTime) // 更新组件流程
}
if(shouldUpdate){
nextChildren = instance.render(); /* 执行render函数 ,得到子节点 */
reconcileChildren(current,workInProgress,nextChildren,renderExpirationTime) /* 继续调和子节点 */
}
}
2.2 getDerivedStateFromProps
在实例化组件之后,会调用 mountClassInstance 组件初始化。在初始化阶段,getDerivedStateFromProps 是第二个执行的生命周期。它是从 ctor 类上直接绑定的静态方法,传入 props ,state 。 返回值将和之前的 state 合并,作为新的 state ,传递给组件实例使用
function mountClassInstance(workInProgress,ctor,newProps,renderExpirationTime){
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode;
const getDerivedStateFromProps = ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps;
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') { /* ctor 就是我们写的类组件,获取类组件的静态方法 */
const partialState = getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState); /* 这个时候执行 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期 ,得到将合并的state */
const memoizedState = partialState === null || partialState === undefined ? prevState : Object.assign({}, prevState, partialState); // 合并state
workInProgress.memoizedState = memoizedState;
instance.state = workInProgress.memoizedState; /* 将state 赋值给我们实例上,instance.state 就是我们在组件中 this.state获取的state*/
}
if(typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps !== 'function' && typeof instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate !== 'function' && typeof instance.componentWillMount === 'function' ){
instance.componentWillMount(); /* 当 getDerivedStateFromProps 和 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 不存在的时候 ,执行 componentWillMount*/
}
}
2.3 componentWillMount
如果存在 getDerivedStateFromProps 和 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 就不会执行生命周期componentWillMount。
function mountClassInstance(workInProgress,ctor,newProps,renderExpirationTime){
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode;
const getDerivedStateFromProps = ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps;
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') { /* ctor 就是我们写的类组件,获取类组件的静态方法 */
const partialState = getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps, prevState); /* 这个时候执行 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期 ,得到将合并的state */
const memoizedState = partialState === null || partialState === undefined ? prevState : Object.assign({}, prevState, partialState); // 合并state
workInProgress.memoizedState = memoizedState;
instance.state = workInProgress.memoizedState; /* 将state 赋值给我们实例上,instance.state 就是我们在组件中 this.state获取的state*/
}
if(typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps !== 'function' && typeof instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate !== 'function' && typeof instance.componentWillMount === 'function' ){
instance.componentWillMount(); /* 当 getDerivedStateFromProps 和 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 不存在的时候 ,执行 componentWillMount*/
}
}
2.4 render
到此为止 mountClassInstancec 函数完成,但是上面 updateClassComponent 函数, 在执行完 mountClassInstancec 后,执行了 render 渲染函数,形成了 children, 接下来 React 调用 reconcileChildren 方法深度调和 children 。
function updateClassComponent(){
let shouldUpdate
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode // stateNode 是 fiber 指向 类组件实例的指针。
if (instance === null) { // instance 为组件实例,如果组件实例不存在,证明该类组件没有被挂载过,那么会走初始化流程
constructClassInstance(workInProgress, Component, nextProps); // 组件实例将在这个方法中被new。
mountClassInstance( workInProgress,Component, nextProps,renderExpirationTime ); //初始化挂载组件流程
shouldUpdate = true; // shouldUpdate 标识用来证明 组件是否需要更新。
}else{
shouldUpdate = updateClassInstance(current, workInProgress, Component, nextProps, renderExpirationTime) // 更新组件流程
}
if(shouldUpdate){
nextChildren = instance.render(); /* 执行render函数 ,得到子节点 */
reconcileChildren(current,workInProgress,nextChildren,renderExpirationTime) /* 继续调和子节点 */
}
}
2.5 componentDidMount
上述提及的几生命周期都是在 render 阶段执行的。一旦 React 调和完所有的 fiber 节点,就会到 commit 阶段,在组件初始化 commit 阶段,会调用 componentDidMount 生命周期
function commitLifeCycles(finishedRoot,current,finishedWork){
switch (finishedWork.tag){ /* fiber tag 在第一节讲了不同fiber类型 */
case ClassComponent: { /* 如果是 类组件 类型 */
const instance = finishedWork.stateNode /* 类实例 */
if(current === null){ /* 类组件第一次调和渲染 */
instance.componentDidMount()
}else{ /* 类组件更新 */
instance.componentDidUpdate(prevProps,prevState,instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate);
}
}
}
}
从上面可以直观看到 componentDidMount 执行时机 和 componentDidUpdate 执行时机是相同的 ,只不过一个是针对初始化,一个是针对组件再更新。到此初始化阶段,生命周期执行完毕。
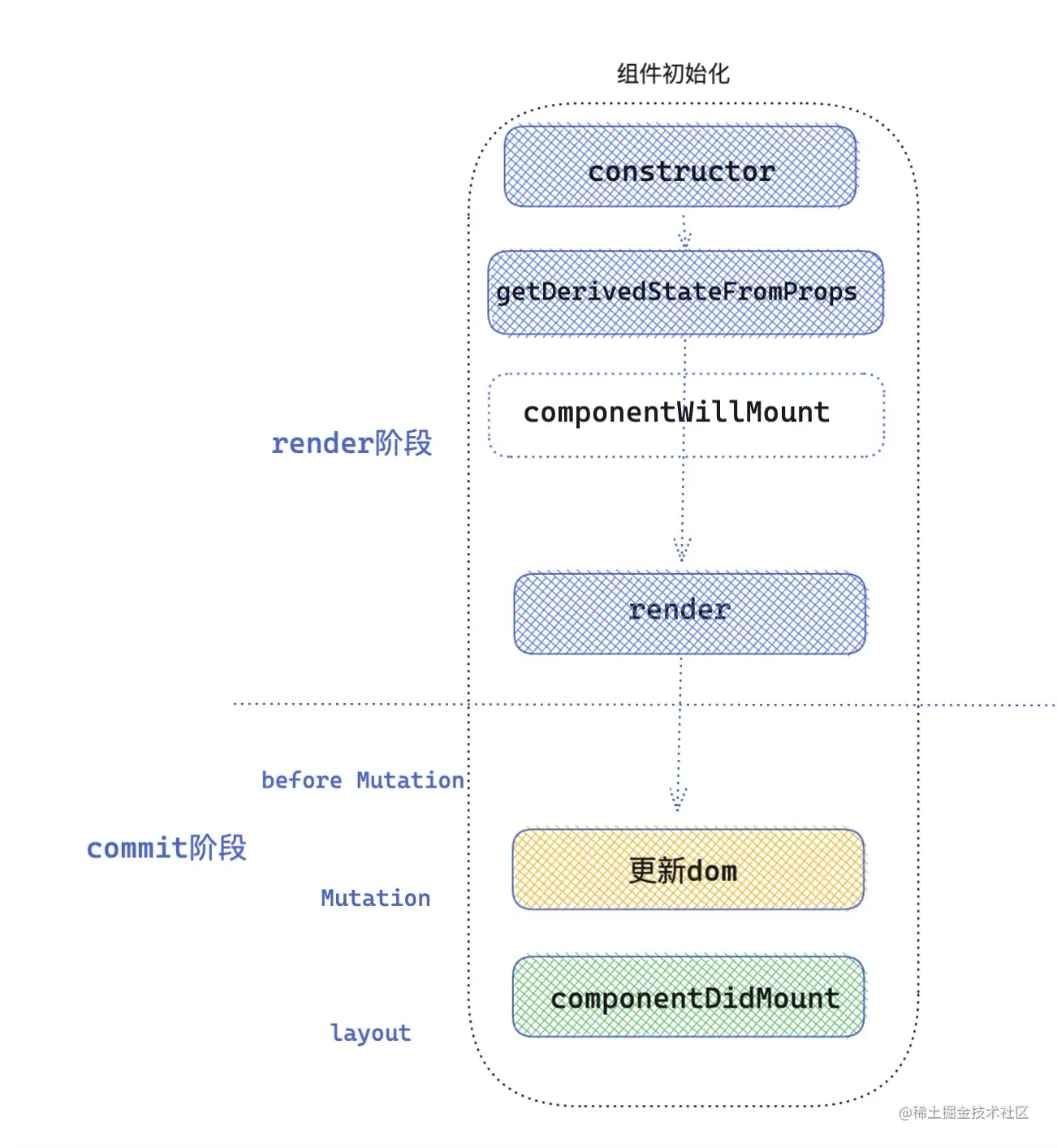
2.6 初始化阶段生命周期总结
初始化阶段,生命周期的执行顺序: constructor -> getDerivedStateFromProps / componentWillMount -> render -> componentDidMount
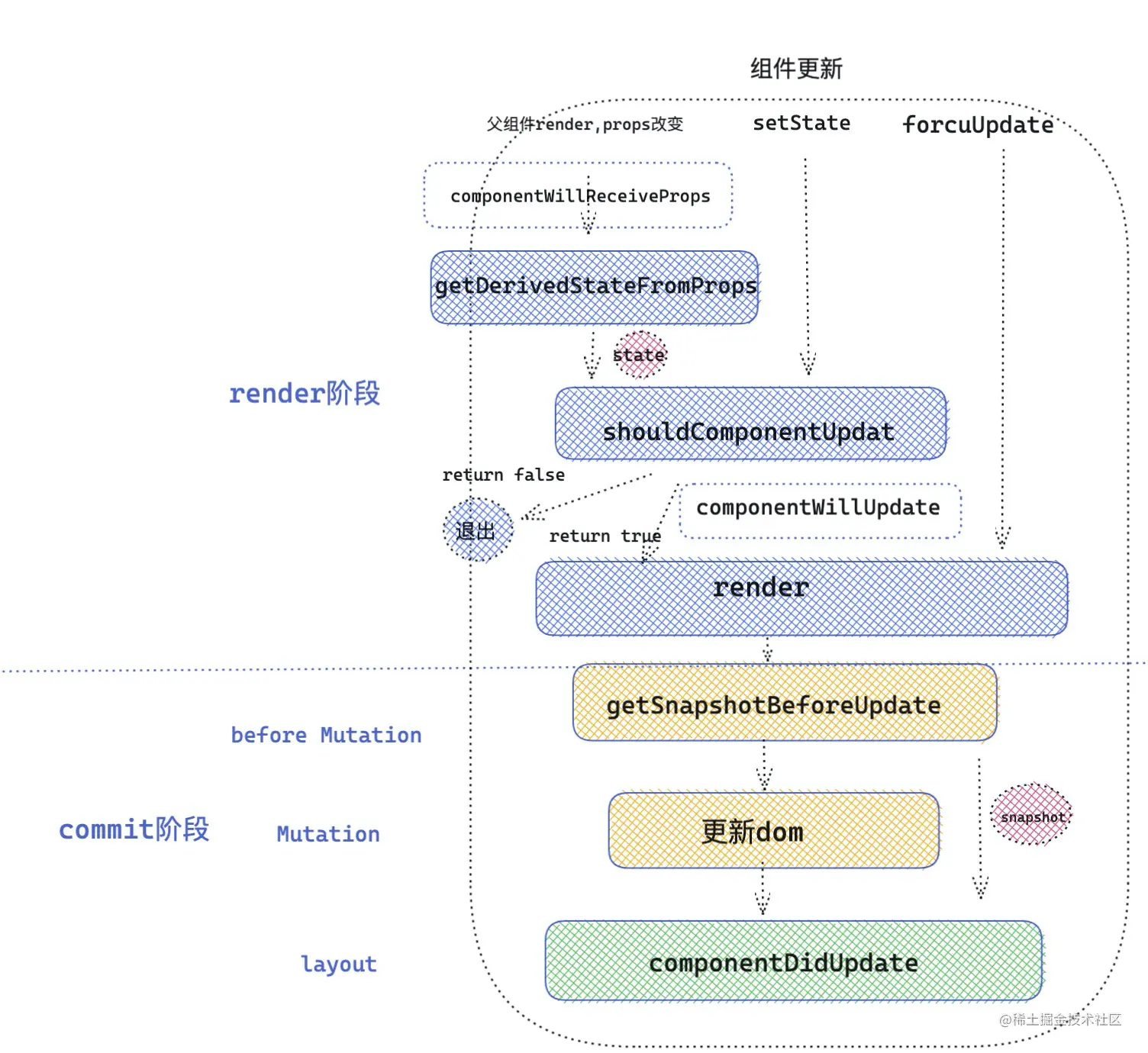
三、update 更新阶段
在一次调和的过程中,发现了一个 fiber tag = 1 类组件的情况,就会按照类组件的逻辑来处理。对于类组件的处理逻辑,首先判断类组件是否已经被创建过,
如果已经创建,那么这个过程就是更新阶段,代码如下:
/* workloop React 处理类组件的主要功能方法 */
function updateClassComponent(){
let shouldUpdate
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode // stateNode 是 fiber 指向 类组件实例的指针。
if (instance === null) { // instance 为组件实例,如果组件实例不存在,证明该类组件没有被挂载过,那么会走初始化流程
constructClassInstance(workInProgress, Component, nextProps); // 组件实例将在这个方法中被new。
mountClassInstance( workInProgress,Component, nextProps,renderExpirationTime ); //初始化挂载组件流程
shouldUpdate = true; // shouldUpdate 标识用来证明 组件是否需要更新。
}else{
shouldUpdate = updateClassInstance(current, workInProgress, Component, nextProps, renderExpirationTime) // 更新组件流程
}
if(shouldUpdate){
nextChildren = instance.render(); /* 执行render函数 ,得到子节点 */
reconcileChildren(current,workInProgress,nextChildren,renderExpirationTime) /* 继续调和子节点 */
}
}
3.1 componentWillReceiveProps
首先判断 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期是否存在,如果不存在就执行componentWillReceiveProps生命周期。传入该生命周期两个参数,分别是 newProps和 nextContext 。
function updateClassInstance(current,workInProgress,ctor,newProps,renderExpirationTime){
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; // 类组件实例
const hasNewLifecycles = typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function' // 判断是否具有 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期
if(!hasNewLifecycles && typeof instance.componentWillReceiveProps === 'function' ){
if (oldProps !== newProps || oldContext !== nextContext) { // 浅比较 props 不相等
instance.componentWillReceiveProps(newProps, nextContext); // 执行生命周期 componentWillReceiveProps
}
}
let newState = (instance.state = oldState);
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') {
ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps,prevState) /* 执行生命周期getDerivedStateFromProps ,逻辑和mounted类似 ,合并state */
newState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
let shouldUpdate = true
if(typeof instance.shouldComponentUpdate === 'function' ){ /* 执行生命周期 shouldComponentUpdate 返回值决定是否执行render ,调和子节点 */
shouldUpdate = instance.shouldComponentUpdate(newProps,newState,nextContext,);
}
if(shouldUpdate){
if (typeof instance.componentWillUpdate === 'function') {
instance.componentWillUpdate(); /* 执行生命周期 componentWillUpdate */
}
}
return shouldUpdate
}
3.2 getDerivedStateFromProps
接下来执行生命周期getDerivedStateFromProps, 返回的值用于合并state,生成新的state。
function updateClassInstance(current,workInProgress,ctor,newProps,renderExpirationTime){
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; // 类组件实例
const hasNewLifecycles = typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function' // 判断是否具有 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期
if(!hasNewLifecycles && typeof instance.componentWillReceiveProps === 'function' ){
if (oldProps !== newProps || oldContext !== nextContext) { // 浅比较 props 不相等
instance.componentWillReceiveProps(newProps, nextContext); // 执行生命周期 componentWillReceiveProps
}
}
let newState = (instance.state = oldState);
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') {
ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps,prevState) /* 执行生命周期getDerivedStateFromProps ,逻辑和mounted类似 ,合并state */
newState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
let shouldUpdate = true
if(typeof instance.shouldComponentUpdate === 'function' ){ /* 执行生命周期 shouldComponentUpdate 返回值决定是否执行render ,调和子节点 */
shouldUpdate = instance.shouldComponentUpdate(newProps,newState,nextContext,);
}
if(shouldUpdate){
if (typeof instance.componentWillUpdate === 'function') {
instance.componentWillUpdate(); /* 执行生命周期 componentWillUpdate */
}
}
return shouldUpdate
}
3.3 shouldComponentUpdate
接下来执行生命周期shouldComponentUpdate,传入新的 props ,新的 state ,和新的 context,返回值决定是否继续执行 render 函数,调和子节点。这里应该注意一个问题,getDerivedStateFromProps 的返回值可以作为新的 state ,传递给 shouldComponentUpdate 。
function updateClassInstance(current,workInProgress,ctor,newProps,renderExpirationTime){
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; // 类组件实例
const hasNewLifecycles = typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function' // 判断是否具有 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期
if(!hasNewLifecycles && typeof instance.componentWillReceiveProps === 'function' ){
if (oldProps !== newProps || oldContext !== nextContext) { // 浅比较 props 不相等
instance.componentWillReceiveProps(newProps, nextContext); // 执行生命周期 componentWillReceiveProps
}
}
let newState = (instance.state = oldState);
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') {
ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps,prevState) /* 执行生命周期getDerivedStateFromProps ,逻辑和mounted类似 ,合并state */
newState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
let shouldUpdate = true
if(typeof instance.shouldComponentUpdate === 'function' ){ /* 执行生命周期 shouldComponentUpdate 返回值决定是否执行render ,调和子节点 */
shouldUpdate = instance.shouldComponentUpdate(newProps,newState,nextContext,);
}
if(shouldUpdate){
if (typeof instance.componentWillUpdate === 'function') {
instance.componentWillUpdate(); /* 执行生命周期 componentWillUpdate */
}
}
return shouldUpdate
}
3.4 componentWillUpdate
接下来执行生命周期 componentWillUpdate。updateClassInstance 方法到此执行完毕了。
function updateClassInstance(current,workInProgress,ctor,newProps,renderExpirationTime){
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode; // 类组件实例
const hasNewLifecycles = typeof ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function' // 判断是否具有 getDerivedStateFromProps 生命周期
if(!hasNewLifecycles && typeof instance.componentWillReceiveProps === 'function' ){
if (oldProps !== newProps || oldContext !== nextContext) { // 浅比较 props 不相等
instance.componentWillReceiveProps(newProps, nextContext); // 执行生命周期 componentWillReceiveProps
}
}
let newState = (instance.state = oldState);
if (typeof getDerivedStateFromProps === 'function') {
ctor.getDerivedStateFromProps(nextProps,prevState) /* 执行生命周期getDerivedStateFromProps ,逻辑和mounted类似 ,合并state */
newState = workInProgress.memoizedState;
}
let shouldUpdate = true
if(typeof instance.shouldComponentUpdate === 'function' ){ /* 执行生命周期 shouldComponentUpdate 返回值决定是否执行render ,调和子节点 */
shouldUpdate = instance.shouldComponentUpdate(newProps,newState,nextContext,);
}
if(shouldUpdate){
if (typeof instance.componentWillUpdate === 'function') {
instance.componentWillUpdate(); /* 执行生命周期 componentWillUpdate */
}
}
return shouldUpdate
}
3.5 render
接下来会执行 render 函数,得到最新的 React element 元素。然后继续调和子节点。
/* workloop React 处理类组件的主要功能方法 */
function updateClassComponent(){
let shouldUpdate
const instance = workInProgress.stateNode // stateNode 是 fiber 指向 类组件实例的指针。
if (instance === null) { // instance 为组件实例,如果组件实例不存在,证明该类组件没有被挂载过,那么会走初始化流程
constructClassInstance(workInProgress, Component, nextProps); // 组件实例将在这个方法中被new。
mountClassInstance( workInProgress,Component, nextProps,renderExpirationTime ); //初始化挂载组件流程
shouldUpdate = true; // shouldUpdate 标识用来证明 组件是否需要更新。
}else{
shouldUpdate = updateClassInstance(current, workInProgress, Component, nextProps, renderExpirationTime) // 更新组件流程
}
if(shouldUpdate){
nextChildren = instance.render(); /* 执行render函数 ,得到子节点 */
reconcileChildren(current,workInProgress,nextChildren,renderExpirationTime) /* 继续调和子节点 */
}
}
3.6 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate
getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 的执行也是在 commit 阶段,commit 阶段细分为 before Mutation( DOM 修改前),Mutation ( DOM 修改),Layout( DOM 修改后) 三个阶段,getSnapshotBeforeUpdate 发生在before Mutation阶段,生命周期的返回值,将作为第三个参数 __reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate 传递给 componentDidUpdate 。
function commitBeforeMutationLifeCycles(current,finishedWork){
switch (finishedWork.tag) {
case ClassComponent:{
const snapshot = instance.getSnapshotBeforeUpdate(prevProps,prevState) /* 执行生命周期 getSnapshotBeforeUpdate */
instance.__reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate = snapshot; /* 返回值将作为 __reactInternalSnapshotBeforeUpdate 传递给 componentDidUpdate 生命周期 */
}
}
}
3.7 componentDidUpdate
接下来执行生命周期 componentDidUpdate ,此时 DOM 已经修改完成。可以操作修改之后的 DOM 。到此为止更新阶段的生命周期执行完毕。
更新阶段生命周期执行顺序: componentWillReceiveProps( props 改变) / getDerivedStateFromProp -> shouldComponentUpdate -> componentWillUpdate -> render -> getSnapshotBeforeUpdate -> componentDidUpdate
四、unmount 销毁阶段
function callComponentWillUnmountWithTimer(){
instance.componentWillUnmount();
}
4.1 componentWillUnmount
销毁阶段就比较简单了,在一次调和更新中,如果发现元素被移除,就会打对应的 Deletion 标签 ,然后在 commit 阶段就会调用 componentWillUnmount 生命周期,接下来统一卸载组件以及 DOM 元素。